PRODUCT Description
Whenever cash is paid out, the Cash account is credited (and another account is debited). Whenever cash is received, the Cash account is debited (and another account is credited). A T-account is a tool used within a ledger to represent a specific account, while a ledger is a complete record of all financial transactions for a company. This prepaid £6000 represents an asset because my landlord owes me 3 months usage of his property since I have paid rent in advance.
- It is typically prepared at the end of an accounting period before financial statements are generated.
- And if you’re new to the accounting world and have little knowledge in finance, T accounts can be especially useful in working through complex financial transactions.
- In the Miscellaneous Expense T-Account, the $1,800 expense amount goes on the left (debit) side of the account because the expense is increasing.
- If they are inaccurate or hard to follow, then everything from drafting financial statements to forecasting future revenue growth is in jeopardy.
- It all comes down to the safety afforded by double-entry accounting.
Automate T Accounts with Online Software
Your profit & loss organises your revenue and expense accounts whilst your balance sheet organises your asset, liability and equity accounts. The double entry process connects these reports together. A single transaction will have impacts across all reports due to the way debits and credits work. So grasping these basics helps you delve into these reports and understand the financial story they tell. The major components of the balance sheet—assets, liabilities and shareholders’ equity (SE)—can be reflected in a T-account after any financial transaction occurs. Liquidity is all about how fast you can turn assets into cash to pay off short-term debts.
- Liabilities, Owner’s Equity and Revenue act in the opposite of them.
- T-accounts can display transactions from a specific time period such as a week or a month.
- This system allows accountants and bookkeepers to easily track account balances and spot errors in journal entries.
- Accounting made simple because it doesn’t have to be hard to understand.
- The first term you’ll want to know is the general ledger.
- T-accounts can be particularly useful for figuring out complicated or closing entries, allowing you to visualize the impact the entries will have on your accounts.
T-Accounts with Single Entries
It ensures every penny is accounted for, keeping the financial records straight. It means what the company owns (assets) is always balanced by what it owes (liabilities) plus what’s left for the owners (equity). Learning the different bank account types and how they differ will help you set up the right system for your personal or business banking needs. A savings account is a great way to start building and growing your savings in an interest earning, secure setting. Once you understand the different types of accounts that banks have to offer, you can decide which type works best for you and your personal and business banking needs. Whether you use T accounts, a general ledger, or both to record every transaction, that’s only the start of monitoring and forecasting your financials.
Create a Free Account and Ask Any Financial Question
For different accounts, debits and credits can mean either an increase or a decrease, but in a T Account, the debit is always on the left side and credit on the right side, by convention. Debits and Credits are simply accounting terminologies that can balance t account example be traced back hundreds of years, which are still used in today’s double-entry accounting system. Once journal entries are made in the general journal or subsidiary journals, they must be posted and transferred to the T-accounts or ledger accounts.
- This is because the types of financial documents both businesses and governments require cannot be created without the details that a double entry system provides.
- Each business transaction is broken into parts with each part being assigned to an account.
- The chart below shows the complete set of T-accounts for the example transactions discussed in this article.
- T-accounts extend beyond basic ledger entries, encompassing a wide array of financial records, including assets, liabilities, equity, revenues, and expenses.
- T-accounts are a colloquial word for a set of financial records that use double-entry accounting.
- The debits are always transferred to the left side and the credits are always transferred to the right side of T-accounts.
Due to the fortunate ‘T’ shape, these diagrams can be used to map out transactions before they are posted into the company’s ledgers to ensure they are correct. Okay, for the first transaction, there will need to be a credit to the Cash T account for $300 and a debit to an equipment T account for $300. Let’s say you want to account for the activities of Busy Bee Bakery and for the example’s sake, they have $500 in their cash account. Since cash is an asset, your debits go on the left and credits on the right.
Example 3 – Paying rent
A double entry system is considered complex and is employed by accountants or CPAs (Certified Public Accountants). The information they enter needs to be recorded in an easy to understand way. This is why a T account structure is used, to clearly mark the separation between “debits” and “credits”. A double entry system is a detailed bookkeeping process where every entry has an additional corresponding entry to a different account. Consider the word “double” in “double entry” standing for “debit” and “credit”.
- Here’s an example of how each T-account is structured in the accounting equation.
- T-accounts are essential for guaranteeing the dependability and correctness of financial data since they systematically record transactions.
- Your account total balance is the previous day’s ending balance, given all fully processed transactions.
- This ensures a complete record of financial events is tracked and can be accurately represented by financial reports.
- When learning the accounting process, from debits and credits to double-entry, it’s easy to get lost in the process and miss the big picture.
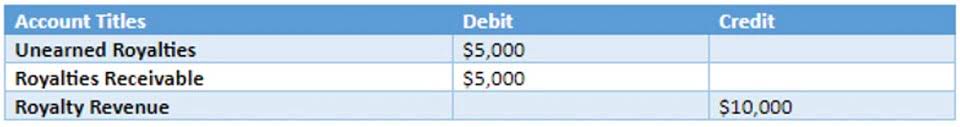
- My bank account is credited £4000, whilst the accounts payable account is debited £2000 and rent is debited £2000.
For example, if your checking account is in overdraft then you have negative cash, which would show a balance on the right side instead. It basically means you have a cash liability instead of asset, which is not good. T accounts are clear, visual representations of a business transactions that take the form of a “T” – one side for debits, one for credits. In this image, you can see a T-account which shows my bank account for the first week of March. Every day, I receive cash from my coffee sales shown in the debit column on the left.
Do you already work with a financial advisor?
And if you’re new to the accounting world and have little knowledge in finance, T accounts can be especially useful in working through complex financial transactions. The use and purpose of a T account is to help business owners visualize the amounts on each individual account. Splitting out debits and credits makes it easier to quickly spot things when looking at the ledger. In double-entry bookkeeping, every transaction affects two accounts at the same time (hence the word double). One of these accounts is always debited, while the other always credited.
- - 574
- ! Без
- ! Без рубрики
- !Fortune tige
- "fc Seoul Vs Jeju United Match Prediction & Betting Ideas With Live Odds - 490
- "mostbet Az-90 Kazino Azerbaycan Lap Yüksək Bukmeyker Rəsmi Sayt - 878
- "mostbet En Vivo: Haz Tus Pronósticos Sobre Directo Y Disfruta De Su Buffering" - 786
- +btoct
- +novPU
- 1
- 1win
- 1Win AZ Casino
- 1Win Brasil
- 1win Brazil
- 1WIN Casino Brasil
- 1win India
- 1WIN Official In Russia
- 1win Turkiye
- 1win uzbekistan
- 1winRussia
- 1wins-moldova.mdro-md x
- 1x-bet.downloa
- 1xbet egypt
- 1xbet Russian
- 1xbet3
- 1xbet32
- 1xbet4
- 1xbet51
- 1xbet52
- 1xbet61
- 1xbet62
- 1xbet82
- 2
- 2024te-Yeni-Üye-Olmanın-Avantajları-Deneme-Bonusu-Veren-Casinoslar.html
- 20Bet Deutschland
- 212
- 222
- 22bet Schweiz
- 26
- 2nd level
- 3
- 3dinvesting.com
- 4
- 5
- 5trucks.ru 500
- 6
- 7 slots
- 7slots
- 7к-казино
- 8
- 9
- a16z generative ai
- a16z generative ai 1
- acad
- Accessories
- adaptationfestival.gr
- adm
- adobe generative ai 1
- adobe generative ai 2
- afyonsosyetepazari.com 1
- AI Chatbot News
- AI News
- aliexpres.com.ua - офіційний сайт Аліекспрес в Україні
- alizeyeniufuklar.com
- almaradio.gr
- amminex.net 2
- amnistiepdm.org - Official Website of Safe Casino Sites in South Korea
- anbhoth.ie
- ankaratarotfali.com 2
- antalyaerenhali.com 1
- antalyaerenhali.com 2
- anushkatrivedi.comen-bd x2
- Apex-Clover-Link-Slot-Oyna---Kazançlı-Çevrimler.html
- archpoints.gr
- Artificial intelligence
- Artificial intelligence (AI)
- asian brides
- augustent.com 1
- Ausländische Online Casinos Schweiz – siehe offizielle Website fanarbeit.ch
- auto-info.hr 2
- aviator-game-official.netlify.app 1
- aviatorSITESI_may
- axiomaltd.ru 1500
- Bahigo Schweiz
- ballybunionartsfestival.ie bCasino
- bambturkiye.com 1
- BankOnBet
- bashpirat.ru 2000
- batery.org.in3
- BC.GAME Casino Schweiz
- bedava-slot-siteleri.com 1500
- bedava-slot.com 1500
- bedpage
- behar.hr 2
- belanok.mk
- best-news
- besyohocam.com 2
- bet10
- bet10 casino
- bet10-casino
- bet442casino.co.uk - UK
- Betmgm Bonus Code Nyp1500dm Grants A 20% Deposit Match Or $1, 500 Initial Bet For Broncos-saints 'thursday Night Football' - 862
- Betonred Casino Schweiz
- betspecial.co.uk 2
- Betting Company Mostbet App Online Sports Betting - 111
- bh_aug
- bh_sep
- bhnov
- bhoct
- BHS-Links
- BHTopJun
- Big-Bass-Bonanza-Blaze-Oyun-İncelemesi.html
- Big-Bass-Bonanza-İkili-Kazanma-Stratejileri-ve-İpuçları.html
- Bigger-Bass-Bonanza-Oyna-Ücretsiz---Slots-Oyunu.html
- bilimufku.com 2000
- biznisakademija.hr
- biznisakademija.hr 2
- Bizzo Casino – Offizielle Website in der Schweiz – editori-sesi.ch
- Bizzo Casino Schweiz
- black-seo-links
- Blog
- Blog Lk
- bonanzasitesi_may
- Bonus-Veren-Casino-Oyunları-En-İyi-Seçenekler.html
- Bookkeeping
- Bookmaker Şirkəti Mostbet: Formal Mobil Versiya Icmalı - 336
- bootstrap-3.rucss.php 900
- borka.org.mk
- braintreerec.com2
- brunch-cafe.ru
- BT_Prod_aug
- bt_sep
- btbtnov
- BTTopJun
- Buon Ma Thuot Itinerary: Explore Buon Ma Thuot in 1,2,3, and 4 Days - 115
- Buon Ma Thuot Itinerary: Explore Buon Ma Thuot in 1,2,3, and 4 Days - 534
- cam-girls
- camp-hockey.ru 500
- campionsbb.com 2000
- cashwin casino schweiz
- casino
- casino en ligne fr
- Casino Mostbet Mostbet Kaszinó Értékelés Nagy Nyeremények És Könnyű Kifizetések Mostbet - 733
- casino onlina ca
- casino online ar
- casinò online it
- Casino Oyunları Giris Yukle Bonuslar - 3
- casino-bet10
- Casino-Oyunlar-ve-Slot-Stratejileri-Şansınızı-Artırmanın-Yolları.html
- casinogermanyforpoland
- casinos
- Casinozer Avis +350 + Fondamental Libéralisation Spins Offert 100% Gratuit - 146
- catcasino-mix
- catcasino4
- cc-women-hellas-virtual-events.gr
- ccasino
- cdradvocacy.org
- centralrest.ru 500
- cerkezkoyisilanlari.com 1500
- CH
- Chathub
- Chatib
- chiorc.gr
- CHjun
- christofilopoulou.gr
- chytayemotut.com.ua
- CIB
- ciroblazevic.hr
- Cities
- City COCO
- content2
- Coolzino Casino Schweiz
- creativeworkingplayground.com
- creativeworkingplayground.com 1000
- Cryptocurrency exchange
- Cryptocurrency News
- czbrandss
- Dede-Casino-Kumar-Oyunu-Gates-of-Olympus-Slot-ile-Eğlenceyi-Zirveye-Taşıyın.html
- Deneme-Bonusu-Veren-Siteler-Kazanç-Fırsatlarını-Keşfedin.html
- dirty-talk
- dkmarino.ru 2000
- dogakentkres.com 2
- drop sk, cz
- drugs
- dutchbikeshop.ie Casinoly
- EC
- Echat
- ecospace
- eda-52.ru 500
- edirectory.ie
- Education
- Efsane-Slot-Oyunlar-ve-En-İyi-Kazandırma-Zamanları.html
- Efsanevi-NetEnt-Slot-Oyunlarıyla-Heyecan-Dolu-Bir-Yolculuğa-Çıkın.html
- Efsanevi-Slotlar-Pragmatic-Play-İle-Şansınızı-Deneyin.html
- egt-casino
- EGT-Slot-Oyunları-Eğlence-Dolu-Bir-Dünyaya-Adım-Atın.html
- ekaterina-school.ru
- Electric Motorbike
- Electric Scooter
- Electric Golf Scooter
- Electric Motorcycle
- Electric Tricycle
- Fat Tire Motorcycles
- Mini Electric Scooter
- elena-kapustina.ru 500
- elysiondanismanlik.com 1000
- en-iyi-slotlar.com 1500
- en-kazanl-slot-oyunlar-66b19ona.net 1000
- epilepsi
- epilepsie
- epilessia
- eporner
- Essentiel Casino En Tracé Langue Super Essentiel Répertoire De Août 2024 - 446
- ethnicitycelebration.ie MyStake
- Exploring Mostbet App In India: A Thorough Guide - 788
- ən Yüksək Mastercard Kazino Azərbaycan 2024 ️ ən əla Mastercard Onlayn Kazinoları - 389
- Fairspin-casino
- fapello
- fast
- festivalaki.gr
- find a bride
- findpolice.ru 700
- FinTech
- fishingbaits.ru 2000
- Forex Trading
- free_spins_free
- fruitslotpaly.com
- Future Trends In Crypto Wallets: Whats Next For Ironwallet? By Investing Com Studios - 149
- g
- galernaya20.ru 600
- games
- gates-of-olympus-oyna-demo.com 1000
- gates-of-olympus-oynayanlar
- Gates-of-Olympus-Slot-Dede-Casinoda-Büyülü-Bir-Kumar-Deneyimi.html
- generacijanext.hr 2
- gennaiapaidia.gr
- genunlimited.mk
- geratalentos.pt
- gerbera.cc
- ggokpoker-ru.ru
- ggpoker-ru.ru
- girls-do-porn
- golden-bet-casino.fr - FR
- goteborgwok.se
- haciozkan.com 1000
- hashtagmafia.de
- HellSpin Casino Official Global Website
- heylink.memostbet-giris_may
- Homepage
- httpsbass-bet.eu.comhubonus - HU
- httpsbass-bet.eu.comhumobile - HU
- httpsbass-bet.eu.comhuslots - HU
- httpsbass-bet.eu.complbonus - PL
- httpsbass-bet.eu.complslots - PL
- httpsenergycasino.eu.comhulogin - HU
- httpsenergycasino.eu.complbonuses - PL
- httpsenergycasino.eu.compllogin - PL
- httpsposido-casino.eu.comes - ES
- httpsposido-casino.eu.comeslogin - ES
- httpsposido-casino.eu.comesmobile - ES
- httpsposido-casino.eu.comfr - FR
- httpsposido-casino.eu.comfrlogin - FR
- httpsposido-casino.eu.comfrmobile - FR
- httpsspinanga.eu.comesbonus - ES
- httpsspinanga.eu.comeslogin - ES
- httpsspinanga.eu.comitbonus - IT
- httpsspinanga.eu.comitlogin - IT
- httpswonaco.eu.comfrbonuses - FR
- httpswonaco.eu.comfrmobile - FR
- httpswonaco.eu.comhubonuses - HU
- httpswonaco.eu.comhumobile - HU
- IGAMING
- igry-nardy.ru
- ihnk.ru 700
- ikranalchik.ru 500
- infopot.ru 2500
- inquisitivereader.com z1
- inquisitivereader.comapp z2
- intellectplanet.ru 1500
- Interwetten Schweiz
- iOS-Mobil-Ödeme-Bahis-Siteleri-Rehberi-2024(2).html
- ireland2040.ie 1Bet
- irelandskillslive.ie Rolletto
- iskonstrukcije.hr
- istoriyaplanety.ru 500
- IT Education
- IT Vacancies
- IT Вакансії
- IT Образование
- IT Освіта
- italyanmutfagihaftasi.com 1
- ivermectina
- Ivermectine
- IviBet Schweiz
- Jeetcity casino schweiz
- jk-yagoda.com.ua
- Jogos E Bônus Do Casino Mostbet Pt - 328
- joomla-school.com
- july_bh
- july_bt
- july_rb
- kartonbardakci.net 1000
- kasyno
- Kasyno Online PL
- kazino-onlayn-reyting-luchshih.xyz 2
- kazino-onlayn-reyting.xyz 2
- keepaneye.mk
- kentt.xyz
- kgskouskosh3.ru 4000
- king johnnie
- klen
- konteynerimalatsatis.com 1000
- kromatografi2023.org 1
- kspb2
- kumar-siteleri(1)_1
- kuzeyyrentacar.com 1500
- latin dating
- Learn English Online Together With Native Level Teachers - 311
- legal-casino-siteleri_1_1
- lenovo-smart.ru 2000
- leramiss
- lightnovosti.ru 170
- list crawler orlando
- Listcrawler central jersey
- listcrawler corpus christi
- Listcrawler san diego
- Lotoclub
- lovepang.ie Malina
- luckhome.ru 2000
- luckyladycharm.hr
- machintech.ru
- machintech.ru 500
- magnosolv.hu x
- mail order bride
- mail order wife
- mais2 com
- maisondecharme.ru 1000
- manaki.mk
- marios-grosser-traum.de
- Marsbahissitesi_may
- max-millions.co.uk - UK
- melbet-app.pro2
- melbetapppk.com
- melbetapppk.comen-pk x2
- melbetcanada.org2
- Meritking-Rulet-ve-Sorumlu-Oyun-Dikkat-Edilmesi-Gerekenler.html
- Metefe-ile-Casino-Sitelerinde-Hızlı-Para-Çekme.html
- Mini Bike
- missionaguafria.com
- missionaguafria.com6
- mobil-slot.com 1500
- mobileporngames
- Monro-casino
- Moonwin Casino – Offizielle Seite in Deutschland
- Mosbet: Onlayn Kazino Və Idman Mərcləri - 232
- Mosbet: Onlayn Kazino Və Idman Mərcləri - 815
- Mostbet £5 Free Bet No Deposit Every Day Of The Cheltenham Festival - 178
- Mostbet Affiliate Program Online Bookmaker Mostbet Partners - 124
- Mostbet Affiliate Program Online Bookmaker Mostbet Partners - 773
- Mostbet Affiliate Program: Ultimate Guide For Success - 254
- Mostbet Agent App Download - 968
- Mostbet App Apk Bangladesh Download For Android 2023 - 869
- Mostbet App Download 2024 Free Online Update V6 53 - 875
- Mostbet App Download Apk For Android And Ios - 310
- Mostbet App Download For Android Apk And Ios 2023 - 545
- Mostbet App Download For Android Apk And Ios In Bangladesh - 627
- Mostbet App Download In Pakistan Mostbet Apk For Android - 830
- Mostbet App Download Is Your Gateway To Immersive Casino Gaming - 544
- Mostbet App Download Is Your Gateway To Immersive Casino Gaming 【中途採用ノウハウ】 リクルートエージェント - 886
- Mostbet AZ Casino
- Mostbet Az-90 Kazino Azerbaycan Daha əla Bukmeyker Rəsmi Say - 660
- Mostbet Az-90 Kazino Azerbaycan Lap əla Bukmeyker Formal Sayt วิปัสสนาภาวนาธรรมโมลี - 806
- Mostbet Azerbaycan Yukle Android Apk Və Ios App-d - 248
- Mostbet Bangladesh Application For Android And Ios - 763
- Mostbet Bangladesh Official Site Sports Betting And Casino Freebets And Freespins - 799
- Mostbet Bd Internet Affiliate Marketing For The Partners Études Romanes : Cahiers Numériques De La Jeune Recherche - 278
- Mostbet Betting Company And Casino In Egypt Play And Make Bets - 231
- Mostbet Bonus Code Acquire Up To $1, 000 Bonus Bets - 160
- Mostbet Bonus Code Postnews: Snag $200 In Bonus Bets Or Perhaps $1k Bet Insurance For Yankees-guardians Sport 3, All Sports - 170
- Mostbet Bonus Program Code Rotowire: Get $1000 Promo Cowboys-browns & More Nfl Odds - 138
- Mostbet Cash Earn Money With Mostbet Via Mobcash App - 598
- Mostbet Casino Almost All Inclusive Μπόνους Για Την Πρώτη Κατάθεση - 794
- Mostbet Casino Online ⭐ Register And Get Welcome Bonus Now - 120
- Mostbet Casino Online ⭐ Register And Get Welcome Bonus Now - 252
- Mostbet Casino: Best Slots 2024 App Login - 205
- Mostbet Casino: актуальные зеркала на сегодня, регистрация, вход, скачать Aarambh Corporate Pvt Ltd - 27
- Mostbet Cheltenham Festival 6th Horses Daily Problem Win Approximately £250k" - 315
- Mostbet Com Live-casino In Bangladesh: Real Casino Action Online! - 70
- mostbet Com Sports Betting On The App Store - 233
- Mostbet Ghana Review Totally Free Bets Up In Order To Ghs 200 Oct 2024 - 875
- Mostbet Giriş Mostbet Türkiye Güncel Giriş Adresi - 999
- Mostbet Kaszinó Online Hivatalos Oldal Mostbet Casino Hungary Nyerőgépek, Bónuszok, Bejelentkezés - 312
- Mostbet Login To Your Online Casino Personal Account In Bangladesh! - 432
- Mostbet Mobil Tətbiq: Azərbaycandan Olan Oyunçular ötrü Icmal 2023 - 639
- Mostbet Mobile App: Review For Players From Azerbaijan 2024 - 963
- Mostbet Nepal: Subscribe With The 46,000 Rs Welcome Bonus - 824
- Mostbet Online Casino And Betting Platform In Pakistan Mobile App - 684
- Mostbet Online Casino And Betting Platform In Pakistan Mobile App [newline]baixar O Mostbet App Para Android Apk E Ios Grátis - 591
- Mostbet Online Casino And Betting Platform In Pakistan Mobile App [newline]baixar O Mostbet App Para Android Apk E Ios Grátis - 811
- Mostbet Overview 2024 Can A Person Trust This Gambling App?" - 775
- Mostbet Pakistan: Official Sports Betting Site 125% Bonus Login - 743
- Mostbet Partners Affiliate Program Review 2023 Upto 60% Revshare - 811
- Mostbet Partners Reviews Read Customer Service Reviews Of Mostbetpartners - 231
- Mostbet Pennsylvania Casino Added Bonus Code Bookies: Get $500 Match Benefit + 100 Moves For October 18th - 922
- Mostbet Portugal Receba Um Bónus De Até 1400 Pln Na Mostbet Pt Hoje! - 357
- Mostbet Registration How You Can Sign Up & Log In" - 457
- mostbet tr
- Mostbet UZ Kirish
- Mostbet Uzbekistan Официальный Сайт Спортивных Ставок И Онлайн-казино Uz 2023 - 7
- Mostbet Wettunternehmen Und Online-casino In Deutschland - 710
- Mostbet-az 45 Azərbaycanda Bukmeker Və Kazino Reward 550+250f 金州資訊 - 821
- Mostbet-az90 ⭐️giriş Və Bonuslar - 174
- Mostbet-az90 Azərbaycandakı Şirkətin Icmalı - 541
- Mostbet-az91: İdman Mərcləri Və Gir วิศวกรรมสถานแห่งประเทศไทย ในพระบรมราชูปถัมภ์ - 699
- Mostbet: Seamless Gaming Awaits Access Login And Mobile Apps Here! - 100
- Mostbet: Unleash Your Winning Potential With The Best Online Bookmaker - 883
- Mottobet---Türkiyenin-En-İyi-Bahis-Sitesi.html
- MOVIEBLOG
- my-1xbet.com
- my-guitar.ru 500
- new
- News
- Nigeria" - 567
- Nine Casino Official Website
- normel-spb.ru 2500
- nppr.hr 2
- Official rating of licensed and safe online casinos in South Korea
- Official website 22Bet
- Official Website For Sports Betting With Bdt 25,000 Bonus - 718
- Official Website For Sports Betting With Bdt 25,000 Bonus - 746
- Official website of Online Casino Rating in South Korea
- Offizielle 1xbet-Website in der Schweiz
- Offizielle Bewertung ausländischer Online-Casinos in der Schweiz
- Offizielle Bruce Bet-Website in Deutschland
- Offizielle Casinia-Website
- Offizielle Roobet-Website in der Schweiz
- Offizielle Roobet-Website in Deutschland - roobetsportwetten.com
- Offizielle Website BC Game Casino in Schweiz - stadionrestaurant.ch
- Offizielle Website des Buchmachers Rabona in Deutschland - rabonaonline.de
- Offizielle Website des Kingmaker Casinos in der Schweiz
- Offizielle Website des Lemon Casinos in der Schweiz
- Offizielle Website des NV Casinos in der Schweiz
- Offizielle Website des Spinanga Casinos
- Offizielle Website des Sportaza Casino in der Schweiz - lateinturerie.ch
- Offizielle Website von 20Bet in der Schweiz
- Offizielle Website von Bahigo in der Schweiz
- Offizielle Website von Betonred in der Schweiz - betonredcasino.ch
- Offizielle Website von Nine Casino
- okggpoker.lol
- okonlineplay.live
- Omegle
- Omegle cc
- omegle.is
- ondr.pt
- onlayn-kazino-reyting.xyz 1
- onlifezone.com - 대한민국의 라이선스 카지노 사이트 평가를 제공하는 국가도박관리위원회(NGCC)의 공식 정부 웹사이트입니다
- Online Betting Best Wagering Site - 275
- online casino au
- Online Gambling And On The Web Casino Games - 956
- onlinecasinopolska
- onwinsitesi_may
- oooat.ru
- organismosathinas.gr
- ostvarisan.hr
- Oyun-Tutkunları-İçin-En-İyi-Yatırım-Artsız-Casino-Siteleri-Forumda-İpuçları.html
- p0kerdom.wiki
- Pablic
- paratissimaskopje.mk
- pauzazapregled.mk
- Paycell-ile-Casino-Oyunları-Oyna---Kolay-Yöntemler.html
- pbnov
- pboct
- PBTOPJun
- pereezd.pl.ua
- perfume-paris.ru 1000
- pin up casino
- Pin UP Casino AZ
- Pin Up Peru
- pin-up
- pinco
- pinup
- PinUP AZ Casino
- pistolo-casinò.it - IT
- pistolocasinò.it - IT
- planet9.hr 2
- play-7k.live
- play.google.comstoreappsdetailsid=com.pinco.nicotoss_Английский
- playpoker-ru.ru
- playzilla casino schweiz
- plinko
- Plus Grand Essentiel En Ligne Fondamental Bonus Jamais Dépôt Exclusif - 383
- poemsandcrimes.gr
- poker-doms.store
- poker.ok-play-poker.click
- poker.play-online-ok.store
- pokerdom-casino.digital
- pokerdom-cazino.ink
- pokerdom-kaz.store
- pokerdom2.guru
- pokerdom24kz.wiki
- pokerdomkaz.live
- pokerdomkazahstan.biz
- pokerplay-ru.ru
- pokervdom.info
- politklass.ru
- porndude
- porngames
- post
- Posts
- premium-cashback.ru 2500
- processed
- PU_aug
- pu_sep
- pu++
- punov
- pytube.io2
- r7-kasino8.site
- r7kazino.life
- Rabona Schweiz
- radio-krapina.hr
- Rating of licensed and safe casino sites in South Korea on the100bestfleets.com
- rboct
- redtube
- remont-casio.ru 500
- remont-iwc.ru 500
- resilientinvestment.orgcanadaonline-casinos z
- review
- reyting-kazino-onlayn.xyz 2
- reyting-luchshih-kazino-onlayn.xyz 2
- reyting-onlayn-kazino-evropy.xyz 2
- reyting-onlayn-kazino-po-vyplatam.xyz 1
- reyting-onlayn-kazino-rossii.xyz 2
- reyting-onlayn-kazino.xyz 2
- reyting-top-10-onlayn-kazino.xyz 2
- riobet5.xyz
- robocatkaszino.hu - HU
- RoksitesiJun
- Roobet Schweiz
- RTP-Slotlarda-Kazanç-Yüzdesini-Artırmanın-5-Yolu.html
- rybelsus
- Sahabet_may
- samsunservisi.com 1500
- sas
- sch11-krasnochervonniy.ru
- scotlandin.space2
- seanamoni.gr
- Şeker-Patlatma-Oyunu-Bahislerinde-Kazanmanın-Sırları.html
- selectorcasino.lol
- selektor5.xyz 600
- Sentyabr 2023 Vərəq 62 Təzə əhval Media - 774
- seo
- seo-links
- seokaya-in-telegram
- service-plus.fr z1
- service-plus.fr z2
- setembroavidainteira.pt
- sevinf.ru 2
- sexting
- sexy-girls
- SFC
- sinanspor.com 1500
- sistemarabuluculuk.com 1000
- sizzlinghotdeluxe.hr
- Skokka
- skonline
- skopjekreativa.mk
- slot-oyunları-demo.net 1000
- Slot-Oyunlarında-Riskleri-Azaltmanın-Yolları.html
- Slot-Oyunlarında-RTP-Oranı-Kayıplarınızı-En-Aza-İndirin.html
- Slot-Uçak-Oyunu-Aviatoru-Oynamanın-En-İyi-Taktikleri.html
- slottica
- smartline93.ru
- Sober living
- Software development
- sondakikaguncelhaber.com 2
- sourliboom.com
- South Korea Casino Site Recommendations - Kangwon Land Official Site - onlifezone.com
- spankbang
- spbunesco.ru 2000
- spellwin.pl - PL
- spinsy-casino.fi - FI
- spinsycasino-fr.com - FR
- spinsykasyno.pl - PL
- stake-casino-ru.ru
- Starlight-Princess-Pachi-Oyun-İncelemesi-ve-İpuçları.html
- steiko.ru 500
- stromectol
- Sugar-Rush-Slot-Pragmatic-Play-Oyun-İncelemesi(2).html
- svsdvsfg
- Sweet-Bonanza-Açığı-Var-mı-Gerçekler-ve-İpuçları(2).html
- Sweet-Bonanza-Oyununda-En-İyi-Kazandırma-Saatleri-Nelerdir.html
- Sweet-Bonanza-Satın-Alma-Özelliği-Açıklaması(2).html
- sweet-bonanza.best 2000
- Tablet
- tandemngo.gr
- tecrubekonusuyor.net 1000
- teleia.com.gr
- test
- The Best Bookmaker And Online Casino In Germany - 151
- The-Dog-House-Slot-İndir-Ücretsiz-Casino-Oyunu.html
- the-omegle
- thelongeststride com
- thenorthfacemontturkiye.com 2
- tipobet turkiye
- tkokaze.hr 2
- TOP New Zealand online casinos
- top-reyting-onlayn-kazino.xyz 2
- TORRENT
- tr
- Troubleshooting Login Issues About Mostbet - 42
- Türkiyenin-En-İyi-Kumar-Siteleri-2024-Listesi(1).html
- tut-boxing.ru 2000
- uaw-chrysler.com 2
- Uncategorized
- unique casino schweiz
- Unsere neue offizielle Bahigo-Website in der Schweiz - schweizbahigo.ch
- UsaSexGuide
- vavada
- vddsvds
- veshka-adm.ru 1500
- victorbout.ru 500
- VIDEOSTREAMING
- vodka-casino-bonuskod.ru
- voziodsrce.mk
- vulcn.pro 2000
- vulkan-casino
- vulkn.online 2000
- vulkn.xyz 2000
- vullkan-lapsha
- Wettigo Schweiz
- What Does The Stage Spread Mean? - 756
- wielosfer.pl
- Wild-West-Gold-Yasal-Site---Güvenli-Casino-Oyunları.html
- Winning-Strategies-How-to-Use-Demo-Slots-to-Your-Advantage.html
- xamou.gr
- xanax
- xn----7sb3aca9ahcif.xn--p1ai 1500
- xn--80aaaiarepjsfqo6ayv.xn--p1ai 500
- xn--90awgb.xn--p1ai 900
- xn--b1amash.xn--p1ai 2000
- xslot
- xvideos
- Yenilikçi-Slot-Casino-Oyunlar-Eğlencenin-En-Son-Halini-Keşfedin.html
- yk
- ysftesisat.com 2
- zenginsozluk.com
- zoomacasino
- казино
- Комета Казино
- Новости
- Новости Криптовалют
- Новый Актуальный Адрес Входа Для Mostbet Россия В 2023 Году - 918
- Скачать Mostbet на Андроид бесплатно приложение 1Вин на телефон БК 1 Вин - 245
- Скачать Приложение Mostbet Для Android Apk И Ios В 1 Клик 2023 - 260
- Скачать Приложение Mostbet Для Android Apk И Ios В 1 Клик 2023 - 81
- Финтех
- Форекс Брокеры
- Форекс Обучение
- Форекс партнерская программа
- ශ්රී ලංකාවේ Mostbet ඔන්ලයින් ඔට්ටු ඇල්ලීම: Mostbet සමඟ විශාල ජයග්රහණයක් ලබා ගන්න සහ ප්රසාද දීමනා ගන්න - 186
- 카지노사이트 순위 한국에서 가장 인기있는 온라인 도박 플랫폼
- 한국 안전 카지노 사이트 평가
- 한국 정부 승인 최고 안전 카지노 순위는 onlifezone.com 에서만 확인 가능합니다
- 한국에서 허가받고 안전한 온라인 카지노의 공식 등급 - onlifezone.com
+86-15150222860
3rd Floor, Building 1,No.88 Guoshan Street, Guoshan Village, ZhiyingTown, Yongkang City, Jinhua City, Zhejiang Province, China